Table of Contents
- Illinois Renters’ Rights and Landlord Responsibilities
- Illinois Landlords’ Rights and Tenant Responsibilities
- Application Fees
- Criminal Background Checks
- Security Deposit
- Late Rent
- Disclosures
- Illinois Lease Agreement Example
- Illinois Landlord-Tenant Law FAQ
- Due Diligence and Illinois Rental Laws
- Illinois Landlord Resources
Illinois is known as the Land of Lincoln – Chicago, in the northeast part of the state, provides a great cultural and economic hub while other parts of the state are rich with agriculture and natural resources. The cities and many suburbs in Illinois are great places for investors to consider buying a rental property as there are options for every budget.

Laws that impact the rental market, landlords, and tenants are constantly being decided in states. Make sure you know what’s on your ballot – find Illinois voting information.
Illinois Renters’ Rights and Landlord Responsibilities
- Return security deposit within 45 days
- You cannot raise the rent on a fixed lease
- Must give tenants 5 days to pay rent before filing for eviction
- If the landlord fails to pay utilities, the tenant can pay and deduct the cost from their rent payment
When it comes to Illinois rental laws, there are a few specifics landlords need to know:
- Security Deposits – The landlord is required to return the security deposit in full within 45 days of a tenant moving out. There is no limit to what the landlord can charge as a deposit, but local governments may have caps in place.
- Raising Rent – Landlords cannot raise the rent on fixed leases but are required to supply a seven-day notice for week-to-week renters, or 30-day notice for month-to-month tenants.
- Eviction – If the reason for eviction is a failure to pay rent, the landlord must give the tenant five days to pay. If an eviction is filed because the tenant violates a term on the lease, the landlord must give a ten-day notice.
- Utilities – If not otherwise noted on the lease agreement, the landlord is responsible for paying the utilities. If the landlord fails to pay the utilities, the tenant may pay for them and deduct the cost out of their rent payment.
- Rental Applications (Illinois) – The Illinois Human Rights Act prohibits employers and landlords from inquiring about or discriminating based on non-conviction records, juvenile records, or expunged or sealed records. (775 Ill. Comp. Stat. Ann. 5/1-103 through 5/3-103. as amended by SB1780.)
- Rental Applications (Cook County) – Landlords can no longer include a checkbox on a housing application that asks whether the applicant has a criminal background or not. They must provide a Tenant Screening Criteria before accepting an application fee. Landlords can ask about criminal background after an applicant has been approved, and can reject based on convictions within the last 3 years, first considering relevant factors (nature of crime, severity, etc.) Sex offender restrictions are basis for rejection.
Illinois Landlords’ Rights and Tenant Responsibilities
- Landlord may charge a $10 late fee for rent under $500
- Tenants have 7 days to claim abandoned property
- Tenants must give a 30-day notice before moving out
- The landlord doesn’t have to give a reason for terminating a lease
- Late Rent – If the tenant does not pay rent on time, the landlord may charge a $10 late fee per month if rent is under $500. If rent is over $500, the landlord may charge a $10 late fee plus 5% of the rent per month.
- Abandoned Property – If a tenant abandons personal property after vacating the unit, the landlord must leave the property or store it for seven days. If the landlord deems the property valueless, they may dispose of it immediately.
- Vacate Notice – Tenants are required to give the landlord a written 30-day notice if they plan to move out. If the tenant pays yearly, then the notice must be 60 days.
- Terminating a Lease – The landlord is required to provide a written 30-day notice to the tenant if they plan to terminate the lease. If the landlord fails to provide notice, the tenant may stay in the unit for 60 days.
Application Fees
There is no cap on application fees in Illinois, including within Chicago and Cook County.
Criminal Background Checks
Cook County landlords cannot ask about criminal background until the applicant has been approved for a rental. A landlord can only reject an application based on criminal convictions within the last three years.
Security Deposit
State of Illinois: Illinois landlords outside of Cook County and the City of Chicago must return a security deposit within 45 days. If there are damages, an itemization of all charges and repair receipts or estimates must be returned within 30 days. There is no cap on security deposits amounts, but it is typically 1-2 times the monthly rent. Security deposits must be deposited in an Illinois FDIC institution. If the landlord has 25 or more units, the account must be interest-bearing and returned to the tenant yearly.
City of Chicago: Chicago landlords must return a security deposit within 45 days. If there are damages, an itemization of all charges and repair receipts or estimates must be returned within 30 days. There is no cap on security deposits amounts, but it is typically 1-2 times the monthly rent. Security deposits must be deposited in Illinois FDIC institution bearing interest for the benefit of the tenant. The landlord must disclose the name and address of this bank.
Cook County: Cook County landlords must return of a security deposit along with the itemization of any damages deducted within 30 days. A security deposit can be no greater than 1.5 times the monthly rent. Security deposits must be deposited in Illinois FDIC institution bearing interest for the benefit of the tenant. The landlord must disclose the name and address of this bank.
Late Rent
State of Illinois: If rent is not received by the fifth day when due, a late charge of 5% of the monthly rent can be charged per month.
City of Chicago: If rent is not paid by the second day when due, a late fee of $10 (for rent under $500) or 5% (for rent over $500) can be charged per month.
Cook County: If rent is not paid by the 2nd day when due, a late fee of $10 (for rent under $1,000) or 5% of the monthly rent (for rent over $1,000) can be charged per month.
Disclosures
State of Illinois:
- Disclosure of nature and amount of any concessions (such as allowing someone one free month of rent, allowing the tenant to paint the property for a rent credit, etc.) given.
- Tenants for any unit on the second floor or below must receive a disclosure of known radon in or around the property. A pamphlet on the dangers of radon prepared by the State of Illinois must be attached to the lease accordingly.
- Any shared utilities must be disclosed along with the formula used to calculate tenant’s share.
City of Chicago and Cook County must provide the State of Illinois disclosures listed above and:
- The Residential Landlord Tenant Ordinance Summary must be attached to the lease along with Bed Bug Brochure prepared by the Illinois Department of Health.
Build a State of Illinois, Chicago, or Cook County lease agreement with all of the required disclosures in less than 15 minutes.
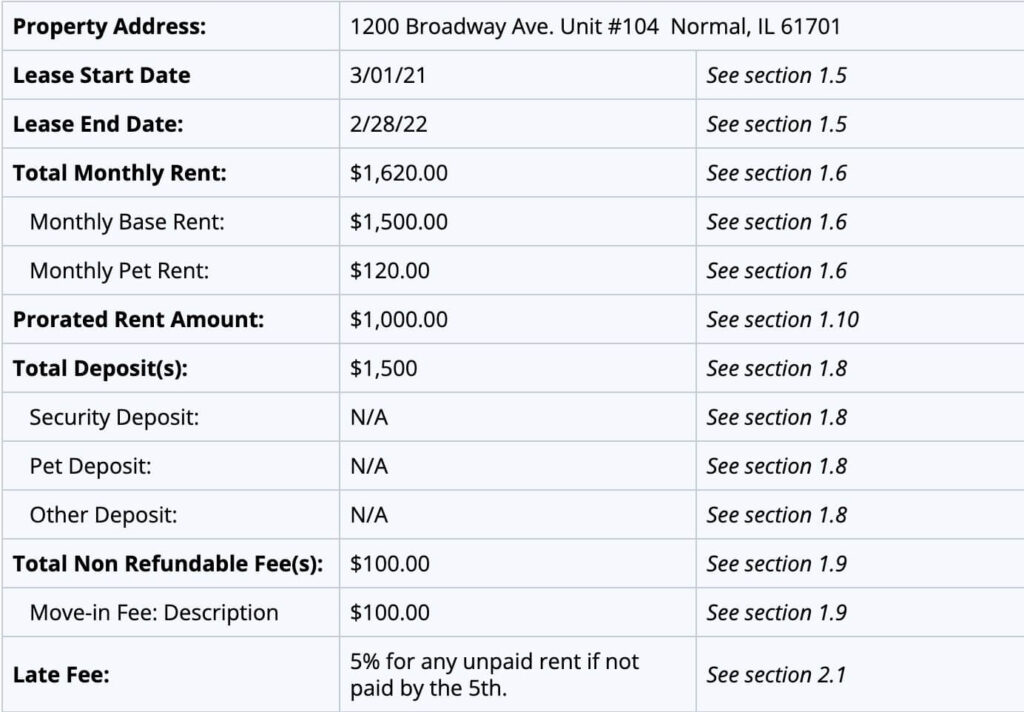
Illinois Lease Agreement Example
There are three sections to a residential lease agreement. The first section outlines the custom details of the contract, such as who’s involved and for what address. Here’s an example Illinois lease agreement listing details found in Section 1:
Illinois Landlord-Tenant Law FAQ
Below are answers to some of the most commonly-asked questions when it comes to landlord-tenant laws in Illinois:
How Long Does a Landlord Have to Fix Something In Illinois?
According to the Illinois Residential Tenants’ Right to Repair Act, a landlord must make the repair within 14 days after being notified by the tenant. If an emergency repair needs to be made, tenants can hire someone to repair the issues, pay the bill, and deduct the payment from their rent.
Can a Landlord Enter Without Permission in Illinois?
In Illinois, a landlord can only enter without permission in case of an emergency – other than that, landlords can enter at a time requested by the tenant during reasonable hours for example between 9:00 am to 8:00 pm. Some cities might have specific rules like Chicago, where a landlord must give a 48-hour notice on their intent to enter the rental property.
What is the Eviction Process in Illinois?
Read the full Illinois eviction laws here. While it can vary on a case-by-case basis, if a tenant fails to pay rent or there is another lease violation, a landlord can start the eviction process – tenants have five days from the day they are first given their eviction notice to pay rent or move out of the rental and then court proceedings may follow.
Due Diligence and Illinois Rental Laws

TurboTenant has utilized many municipal sources along with official state statutes in order to compile this information to the best of our ability. However, local laws are always in flux and landlords and tenants alike should do their due diligence and consult legal help when it’s needed. We hope the following list can serve as a valuable resource and allow you to succeed as a tenant or landlord in Illinois. Be sure to take proper precautions when it comes to finding the top candidates for your unit by utilizing our online rental application and tenant screening services.
Disclaimer: TurboTenant, Inc does not provide legal advice. This material has been prepared for informational purposes only. All users are advised to check all applicable local, state, and federal laws, and consult legal counsel should questions arise.

Unlimited Everything.
Create a single Illinois lease agreement, or subscribe and receive unlimited lease agreements, landlord forms pack, and e-signs for a simple annual fee. Be confident with all the legal forms and tools you need as a professional landlord.
Discover Our Unlimited PlanIllinois Landlord Resources
Illinois Landlord-Tenant Law Resources
- Landlord and Tenant Act – (765 ILCS 705/)
- Landlord and Tenant Rights and Laws – Attorney General Lisa Madigan
- Residential Tenants’ Right to Repair Act – (765 ILCS 742/)
Illinois Fair Housing Resources
Federal Fair Housing Resources
- Federal Fair Housing Act
- United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD)
- Civil Rights Act of 1968 (Wikipedia)
Other State Resources
- Security Deposit Return Act – (765 ILCS 710/)
- Security Deposit Interest Act – (765 ILCS 715/)
- Retaliatory Eviction Act – (765 ILCS 720/)
- Property Taxes of Alien Landlords Act – (765 ILCS 725/)
- Rent Concession Act – (765 ILCS 730/)
- Rental Property Utility Service Act – (765 ILCS 735/)
- Tenant Utility Payment Disclosure Act – (765 ILCS 740/)
- Mobile Home Landlord and Tenant Rights Act – (765 ILCS 745/)
- Safe Homes Act – (765 ILCS 750/)
Illinois Associations
Illinois City-Specific Housing Resources
Chicago
- Residential Landlord and Tenant Ordinance Summary – City of Chicago
- Rents Right – City of Chicago
- Fair Housing and Equity Assessment: Metropolitan Chicago
- Chicagoland Apartment Association
- Chicago Association of REALTORS®
Aurora
Rockford
Joliet
Naperville
- Tenants and Landlords – City of Naperville
- Housing Advisory Commission – City of Naperville
- Three Rivers Association of REALTORS®
Springfield
Peoria
- Tenant Tips and Responsibilities – City of Peoria
- Landlord Information – City of Peoria
- Fair Housing Commission – City of Peoria
- Peoria Area Association of REALTORS®
Elgin