Table of Contents
- Kentucky Renters’ Rights and Landlord Responsibilities
- Kentucky Landlords’ Rights and Tenant Responsibilities
- Rental Application Fee
- Criminal Background Check
- Security Deposit
- Lease Agreement Disclosures
- Kentucky Lease Agreement Example
- Kentucky Landlord-Tenant Law FAQ
- Due Diligence and Kentucky Rental Laws
- Kentucky Landlord-Tenant Law Resources
Population in Kentucky has been growing steadily for the last decade, and it is projected to continue on the same course which makes Kentucky a great place for property investors to invest. The job market and home prices are also projected to increase, which makes purchasing a rental property a great investment.
Laws that impact the rental market, landlords, and tenants are constantly being decided in states. Make sure you know what’s on your ballot – find Kentucky voting information.
Kentucky Renters’ Rights and Landlord Responsibilities
- Tenants have 60 days to claim security deposit
- No notice required before raising rent
- Two-day notice required before entering the property
- Required to make repairs within 14 days
When it comes to Kentucky rental laws, there are a few specifics landlords need to know:
- Security Deposit – Kentucky law does not limit the amount a landlord may charge for the security deposit. Kentucky does require landlords to put the depository in a federally regulated bank but they are not required to pay out the interest gained. Tenants are responsible for claiming their security deposit within 60 days of them moving out.
- Raising Rent – Landlords in Kentucky may increase the rent to any amount for any reason with no notice.
- Notice of Entry – Kentucky requires a two-day written notice from the landlord before entering.
- Repairs – It is the landlord’s responsibility to keep the rental in safe and healthy living conditions. Landlords must make repairs within 14 days of being notified by the tenant. If they fail to do so, the tenant may make the repairs themselves and deduct the cost from their next rent payment.
Kentucky Landlords’ Rights and Tenant Responsibilities
- Tenants have seven days to pay rent after they receive a written notice
- Must give a 30-day notice before terminating a lease
- Tenants must keep the property clean and make small repairs
- Overdue Rent – If a tenant fails to pay rent on time, the landlord must give them a seven-day notice to pay or quit. If the tenant fails to pay, the landlord may file for eviction.
- Terminating a Lease – If a tenant needs to terminate a month-to-month lease, they must give the landlord a 30-day notice.
- Tenant Responsibilities – Tenants are required to keep the property clean and not disturb neighbors.
Rental Application Fee
There are no rental application fee laws in Kentucky.
Criminal Background Check
- HUD (Federal) laws do not classify criminal backgrounds as a protected class, but making a decision to rent based off a criminal background alone could lead to a discrimination charge as it impacts certain protected groups of people disproportionately.
- However, if the criminal background check revealed a crime for the manufacture and distribution of drugs, homicide and/or stalking, denying the application is allowed.
- Landlords should have a consistent and equal policy or procedure in place to follow regarding criminal background checks so as not to discriminate against one class of people over another.
- HUD states that a landlord cannot ask about arrest records, only convictions, as innocent people are commonly arrested though the situation may not have resulted in a conviction.
- Some municipalities may have written their own laws expanding onto what you can and cannot ask regarding criminal backgrounds during the tenant screening process.
Security Deposit
Tenants are responsible for claiming their security deposit within 60 days of moving out after receiving written notification from landlord.
Lease Agreement Disclosures
- Landlords are legally required to disclose the banking institution and account number that holds the tenant’s security deposit.
- If a landlord collects a security deposit, they must provide an inventory of the rental unit’s condition at the start of the lease term.
Build a Kentucky lease agreement in less than 15 minutes.
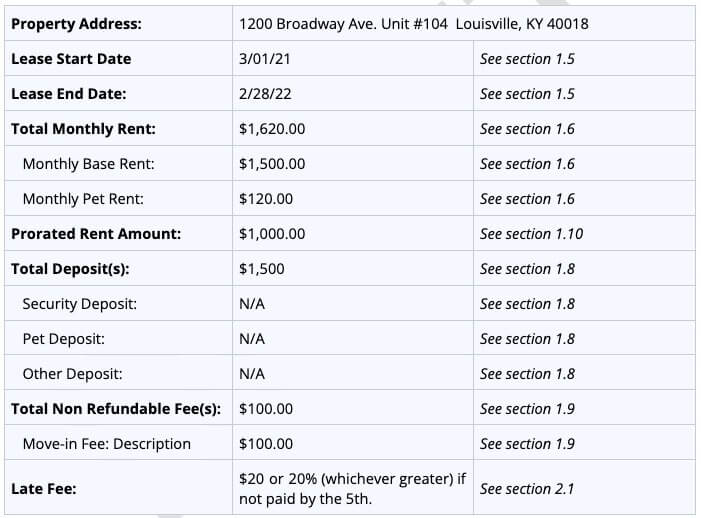
Kentucky Lease Agreement Example
There are three sections to a residential lease agreement. The first section outlines the custom details of the contract, such as who’s involved and for what address. Here’s an example Kentucky lease agreement listing details found in Section 1:
Kentucky Landlord-Tenant Law FAQ
Below are answers to some of the most commonly-asked questions when it comes to landlord-tenant laws in Kentucky:
Can You Withhold Rent in Kentucky?
Renters are able to pay for repairs that the landlord fails to make and deduct up to half of the next month’s rent.
How Long Does it Take to Evict a Tenant in Kentucky?
Evicting a tenant in Kentucky typically takes anywhere from three to six weeks depending on the reason for eviction.
Is Kentucky a Landlord-Friendly State?
Kentucky is considered a landlord-friendly state because of the lack of rent control laws.
What is the Eviction Process in Kentucky?
There are three reasons a landlord may file for eviction in Kentucky. The three reasons include failure to pay rent, violation of the lease agreement, and end of the lease term. Depending on the violation, the landlord must give the tenant notice and anywhere from seven to 30 days to cure their violation.
If the tenant fails to cure or quit, then the landlord may file a complaint with the court, which costs $43. After the complaint is filed, it will be served to the tenant at least three days before the eviction hearing.
If the court rules in favor of the landlord, then a writ of restitution will be issued immediately. Upon being served the writ of restitution, the tenant will have to move out within seven days.
How Much Notice Does a Landlord Have to Give a Tenant to Move Out in Kentucky?
Landlords must give a 30-day notice before asking a tenant to vacate the property.
Due Diligence and Kentucky Rental Laws
TurboTenant has utilized many municipal sources, along with official state statutes, in order to compile this information to the best of our ability. However, local laws are always in flux, and landlords and tenants alike should do their due diligence and consult legal help when it’s needed. We hope the following list can serve as a valuable resource and allow you to succeed as a landlord or tenant in Kentucky. Be sure to take proper precautions when it comes to finding the top candidates for your unit by utilizing our online rental application and tenant screening services.
Disclaimer: TurboTenant, Inc does not provide legal advice. This material has been prepared for informational purposes only. All users are advised to check all applicable local, state, and federal laws, and consult legal counsel should questions arise.
Unlimited Everything.
Create a single Kentucky lease agreement, or subscribe and receive unlimited lease agreements, landlord forms pack, and e-signs for a simple annual fee. Be confident with all the legal forms and tools you need as a professional landlord.
Discover Our Unlimited PlanKentucky Landlord-Tenant Law Resources
- Uniform Residential Landlord and Tenant Act – Kentucky Legislature
- KENTUCKY LANDLORD AND TENANT DUTIES – National Conference of State Legislatures
Kentucky Fair Housing Resources
- Fair Housing Enforcement in Kentucky
- The Fair Housing Handbook
- Kentucky Fair Housing Brochure
- Local Tenant Rights, Laws, and Protections: Kentucky – HUD
- Kentucky – HUD
Other State Resources
Kentucky Associations
Louisville
- The State of Fair Housing in Louisville
- City of Louisville Property Maintenance Checklist
- Louisville Apartment Association
- Greater Louisville Association of Realtors®
Lexington
- Off-Campus Resources | Student Success
- Uniform Residential Landlord and Tenant Act Ordinance No. 98‐84 – University of Kentucky
- Greater Lexington Apartment Association
- Lexington – Bluegrass Association of REALTORS®
Bowling Green
Owensboro
Covington
- Housing Choice Voucher | City of Covington, KY
- No Rental License? Your Time’s Up
- Covington Housing Authority – Better Futures
- Northern Kentucky Association of REALTORS®
Richmond
Hopkinsville
Florence
Federal Fair Housing Resources